LayoutManagerを拡張して曲線上にコンポーネントを配置
Total: 5682, Today: 1, Yesterday: 0
Posted by aterai at
Last-modified:
Summary
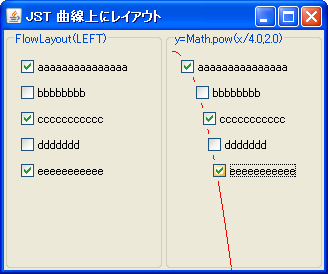
LayoutManagerを拡張して曲線上にコンポーネントを配置します。
Screenshot
Advertisement
Source Code Examples
final double A2 = 4.0;
panel2.setLayout(new FlowLayout() {
@Override public void layoutContainer(Container target) {
synchronized(target.getTreeLock()) {
Insets i = target.getInsets();
int nmembers = target.getComponentCount();
if (nmembers <= 0) {
return;
}
int vgap = getVgap();
int hgap = getHgap();
int rowh = (target.getHeight() - (i.top + i.bottom + vgap * 2)) / nmembers;
int x = i.left + hgap;
int y = i.top + vgap;
for (int i = 0; i < nmembers; i++) {
Component m = target.getComponent(i);
if (m.isVisible()) {
Dimension d = m.getPreferredSize();
m.setSize(d.width, d.height);
m.setLocation(x, y);
y += (vgap + Math.min(rowh, d.height));
x = (int) (A2 * Math.sqrt(y));
}
}
}
}
});
Description
- 左:
FlowLayout(LEFT)new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT)を設定したJPanelにコンポーネントを配置
- 右:
y=Math.pow(x/4.0, 2.0)FlowLayout#layoutContainer(...)をオーバーライドして二次曲線の上にコンポーネントを配置するレイアウトを作成してJPanelに設定