JLabelで文字列のあふれをフェードアウト効果に変更する
Total: 3329, Today: 1, Yesterday: 1
Posted by aterai at
Last-modified:
Summary
JLabelなどで文字列があふれる場合、デフォルトの省略記号…ではなく、フェードアウト効果を適用して端付近の文字を透明表示します。
Screenshot
Advertisement
Source Code Examples
class TextOverflowFadeLabel extends JLabel {
private static final int LENGTH = 20;
private static final float DIFF = .05f;
protected TextOverflowFadeLabel(String text) {
super(text);
}
@Override public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
Insets i = getInsets();
int w = getWidth() - i.left - i.right;
int h = getHeight() - i.top - i.bottom;
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(i.left, i.top, w - LENGTH, h);
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g.create();
g2.setFont(g.getFont());
g2.setPaint(getForeground());
FontRenderContext frc = g2.getFontRenderContext();
TextLayout tl = new TextLayout(getText(), getFont(), frc);
int baseline = getBaseline(w, h);
g2.setClip(rect);
tl.draw(g2, getInsets().left, baseline);
rect.width = 1;
float alpha = 1f;
for (int x = w - LENGTH; x < w; x++) {
rect.x = x;
alpha = Math.max(0f, alpha - DIFF);
g2.setComposite(AlphaComposite.SrcOver.derive(alpha));
g2.setClip(rect);
tl.draw(g2, getInsets().left, baseline);
}
g2.dispose();
}
}
Description
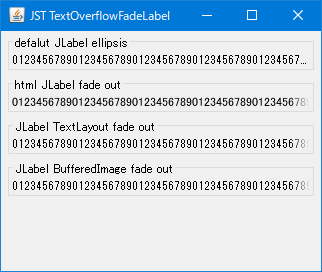
default JLabel ellipsisJLabelのデフォルトは、省略記号…であふれる文字列を省略
html JLabel fade outJLabelの文字列先頭に<html>タグを付加してデフォルト省略記号によるあふれ省略を無効化- 代わりに
JLabel#paintComponent(...)をオーバーライドして、右端付近の文字列をフェードアウト効果で透明化Graphics2D#setClip(...)で描画領域を限定し、幅1px毎にGraphics2D#setComposite(AlphaComposite.SrcOver.derive(alpha))でアルファ値を設定して描画- Fontのアウトラインを取得して文字列の内部を修飾する
Graphics2D#setComposite(...)を使用すると文字列にアンチエイリアスが掛かってしまう?ため、透明化しない文字列にもほぼ1fのアルファ値を設定して描画
JLabel TextLayout fade out<html>タグは使用せず、TextLayoutを生成し直接文字列を描画してあふれ省略を無効化- フェードアウト効果は
html JLabel fade outと同様
JLabel BufferedImage fade outJLabel TextLayout fade outと同様にTextLayoutで文字列を描画して省略記号によるあふれ省略を無効化- 文字列を
BufferedImageに描画し、その右端付近のピクセル値をBufferedImage#getRGB(...)で取得後アルファ成分を変更してBufferedImage#setRGB(...)で戻す
class FadingOutLabel extends JLabel {
private static final int LENGTH = 20;
private final Dimension dim = new Dimension();
private transient BufferedImage img;
protected FadingOutLabel(String text) {
super(text);
}
@Override public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
// super.paintComponent(g);
int w = getWidth();
int h = getHeight();
if (img == null || dim.width != w || dim.height != h) {
dim.setSize(w, h);
img = updateImage(dim);
}
g.drawImage(img, 0, 0, this);
}
private BufferedImage updateImage(Dimension d) {
img = new BufferedImage(d.width, d.height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
Graphics2D g2 = img.createGraphics();
g2.setFont(getFont());
g2.setPaint(getForeground());
FontRenderContext frc = g2.getFontRenderContext();
TextLayout tl = new TextLayout(getText(), getFont(), frc);
int baseline = getBaseline(d.width, d.height);
tl.draw(g2, getInsets().left, baseline);
g2.dispose();
int spx = Math.max(0, d.width - LENGTH);
for (int x = 0; x < LENGTH; x++) {
double factor = 1d - x / (double) LENGTH;
for (int y = 0; y < d.height; y++) {
int argb = img.getRGB(spx + x, y);
int rgb = argb & 0x00_FF_FF_FF;
int a = (argb >> 24) & 0xFF;
img.setRGB(spx + x, y, ((int) (a * factor) << 24) | rgb);
}
}
return img;
}
}